The basic drying process of wet coating on lithium battery sheet is described
Sep 20, 2019 Pageview:1913
The lithium battery electrode is a coating composed of particles. During the preparation of the electrode, a uniform wet slurry is applied to the metal collector fluid, and then the solvent in the coating is removed by drying. Electrode slurry often needs to add polymer binder or dispersing agent, as well as carbon black and other conductive agents. Although the solid content is generally greater than 30%, during the drying process, when the solvent evaporates, the coating will always experience a certain shrinkage, and solid substances are close to each other in the wet coating, finally forming a porous dry electrode structure.
The drying process and coating process of lithium ion battery are independent and interrelated. The nature of the coating affects the design and operation of the drying process; Coating speed, coating thickness determines the drying length; In the drying process, the coating has a leveling process, which affects the coating uniformity. Therefore, coating in the design process can accurately use the best coating, drying process, balance the relationship between the two, and ultimately affect the overall technical properties of coating.
Extremely sheet drying method
(1) Far-infrared radiation drying. The heat energy is radiated to the surface of the dry object by a far-infrared emitting element to vaporize the liquid for drying. Characteristics: its drying speed mainly depends on the radiation temperature, high temperature, fast drying speed. Its advantage is that the equipment is relatively simple, so are relatively low in the application of the coating machine. Its disadvantage is low drying efficiency, uneven drying, easy to produce drying disease.
(2) Double-sided air supply floating and drying. Floating drying is for the drying foil for a special design of double-sided nozzle, high-speed jet flow, under the effect of air flow wall effect, vertical action to the drying foil, under the effect of air flow, dry sheet floating state for drying.
(3) Conventional convection air drying. Convection drying is a more traditional drying technique. The heated dry air is sent into the drying passage, and the heat energy in the dry air is transmitted to the dried object through the convection of the air, and the liquid is vaporized for drying. Its advantage is simple equipment, its disadvantage is low drying efficiency, in the modern drying equipment is gradually replaced by efficient hot air drying.
(4) Circulating hot wind impacts drying. A highly efficient drying technique based on the principles of air jet hydrodynamics. Through specially designed air nozzle, dry air is sprayed to the surface of the dried object at a high speed, and the static air layer impeding drying on the surface of the dried object is destroyed under the impact effect, thus accelerating the drying process and greatly improving the drying efficiency. The characteristic of circulating hot air impact drying is that the drying speed is related to the temperature and the drying air volume. Part of the circulating dry air can be used to increase the air supply to improve the drying speed and greatly improve the utilization of the heat of the dry air. Therefore, the circulating hot air impact drying has the characteristics of high efficiency and energy saving. In addition, the rate of drying can be increased by increasing the air supply.
(5) Superheated steam drying. Superheated steam is the vapor obtained by heating a liquid to the saturated vapor that evaporates it completely and then heating it again. Superheated steam drying is a new drying method in which the drying medium is directly in contact with the wet coating, and the heat is mainly transferred to the material by convection, and the precipitated solvent is carried away by the drying medium. In the drying process, the superheated steam passes through the material surface as the drying medium, and the heat is transferred to the wet coating, and the free solvent on the coating surface is heated and vaporized, thus resulting in the difference between the material surface and the internal moisture content concentration. Under this difference, the internal moisture content diffuses from the liquid or gaseous form to the surface, and the aporized water vapor r vapor is carried away by the superheated steam flow. Its advantage is the latent heat of steam can be used, high thermal efficiency, can achieve the effect of energy saving, superheated steam drying than hot air drying heat transfer coefficient.
(6) microwave drying. Microwave drying is a method that makes use of microwave energy with frequency of 915-2450mhz to make materials heat up and heat up, so as to evaporate water for drying. Microwave drying is different from the traditional drying method, and the direction of heat conduction is the same as that of water diffusion. Compared with traditional drying methods, microwave drying has the advantages of fast drying rate, energy saving and environmental protection, high production efficiency, clean production, excellent drying effect, easy to realize automatic operation and control, and can improve product quality.
At present some manufacturers produce coating machine with hot air drying, also use air nozzle, from the form of drying and impact similar, but the wind nozzle structure design and air volume and wind speed have no impact effect, drying process is still convection drying, drying efficiency is not high.
Classification of moisture in materials
The relationship among total moisture, equilibrium moisture, free moisture, combined moisture and uncombined moisture of materials is shown in figure 1.
Balanced moisture: moisture that can be removed by drying. Free moisture: moisture that cannot be removed by drying.
The combined water includes the water in the cell wall of the material, the water in the capillary of the material, and the water in the solid material in the form of crystal water.
Unbound water includes water mechanically attached to a solid surface, such as water adsorbed on a material surface, water in larger pores, etc.
The fundamentals of drying
Drying: the operation of removing moisture from solid materials by means of heating is to vaporize water or other solvents and to remove the resulting vapor.
The partial pressure of water vapor in the film is equal to the vapor pressure of water in materials. At the same time, the hot air heats up the material and transfers the heat to the wet material. The driving force is the temperature gradient between the hot air and the material. To convective dryness, because of medium ceaseless flow, take away the vaporized water, form cent pressure difference thereby.
The necessary condition for the drying process to be carried out is that the partial pressure of water vapor generated by the moisture in the dried material is greater than that in hot air. If they are equal, evaporation reaches equilibrium and drying stops. If the partial pressure of water vapor in hot air is large, the material absorbs water instead.
The drying process of materials is a process combining heat transfer and mass transfer:
(1) heating of materials by hot air;
(2) evaporation and vaporization process of material surface liquid;
(3) Diffusion of internal liquid through pores to the surface.
The kinetic process of drying
Drying curve: the relation curve of material moisture content x in the drying process is to drying time t and material surface temperature t.
Drying rate curve: the relationship curve between material drying rate u and material moisture content X.
The internal diffusion and surface vaporization of water occur simultaneously, but the rate is different at different stages of the drying process, so the mechanism of controlling the drying rate is also different. The drying process is divided into preheating heating section AB, constant speed drying section BC and slow drying section CDE.
(1) AB in the preheating and warming stage: the material is heated and heated
(2) the constant speed drying stage BC: be dry material surface is always kept wet water evaporation, the steam in the quantity of heat is absorbed by the material, all this heat is used to evaporate moisture on the surface of the material, material surface moisture evaporating speed and material internal moisture diffusion velocity is almost equal, drying rate remained stable at this point, constant speed dry state.
(3) The first deceleration stage (section CD) : the internal water diffusion rate of the material is lower than the evaporation rate of the surface water at the wet-bulb temperature. At this time, the surface of the material cannot be kept fully wet and a "dry zone" is formed, resulting in a decrease in the drying rate.
(4) Second deceleration stage (DE stage) : the evaporation surface of water gradually moves towards the interior of the material, thus lengthening the heat and mass transfer paths and increasing the resistance, resulting in a decrease in the drying rate.
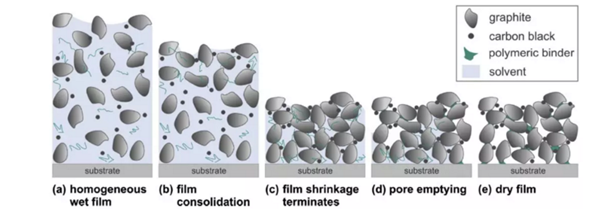
FIG. 5 schematic diagram of pole sheet drying process
Lithium battery electrode paste composition is uniform distribution, then, the solvent evaporation induced wet coating thickness decreases, the graphite particles gradually close to each other, until the formation of the accumulation of the most densely populated state, coating contract termination (FIG. 5 c), then pushed further solvent evaporation forced the gas-liquid interface to the pore structure inside, eventually forming porous coating on dry electrodes (FIG. 5 e). The big hole tend to preferentially empty the liquid phase. In the process of coating shrinkage, the small pores on the surface are filled with liquid phase, until the coating shrinkage stops (FIG. 5c) and the pores are filled with solvent. The solvent is then further removed, creating the first larger hole in the coating (FIG. 5d), while the smaller hole is more difficult to empty due to capillary forces.
The page contains the contents of the machine translation.
Leave Message
Hottest Categories
-
Hottest Industry News
-
Latest Industry News









